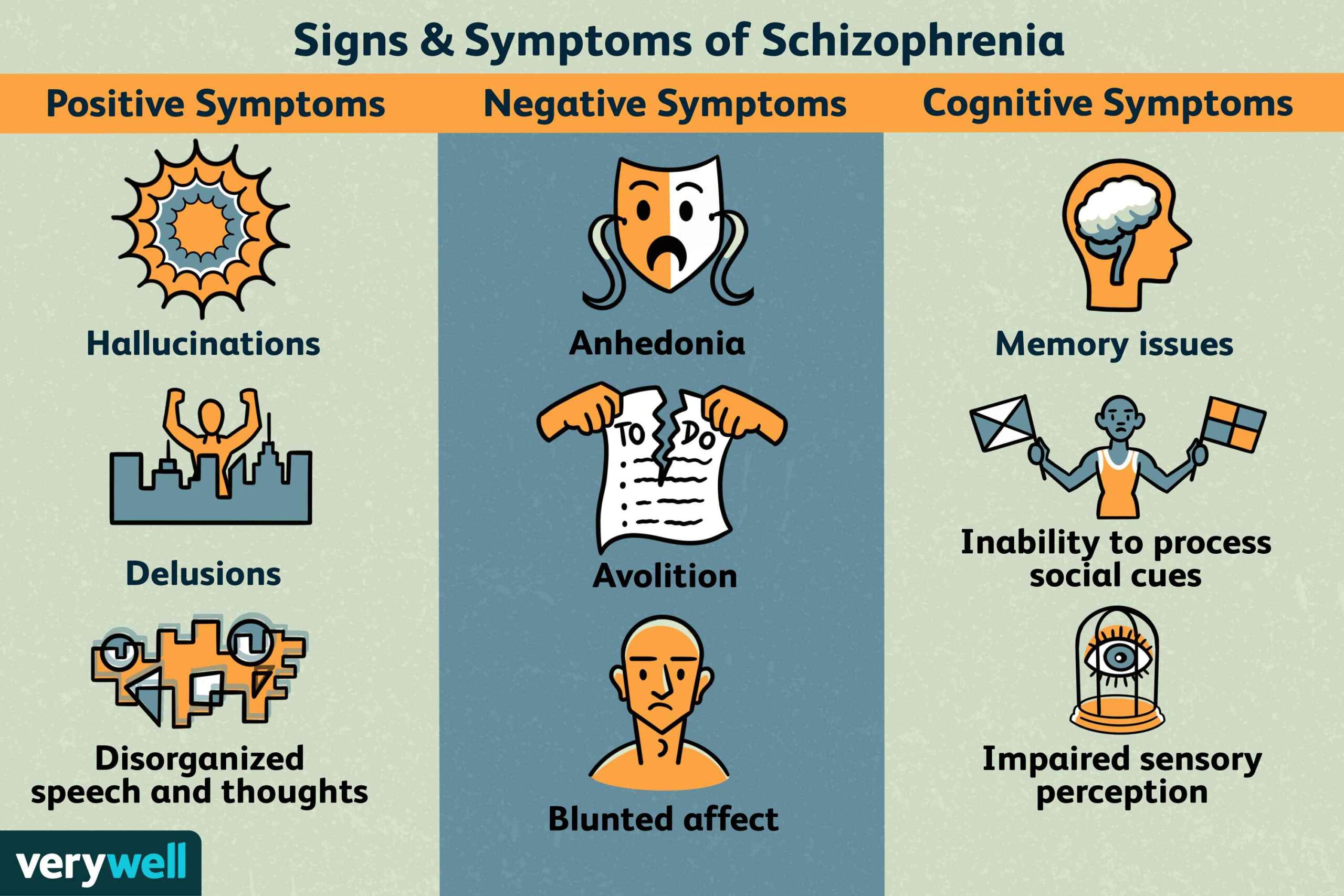
Current treatments for Schizophrenia focus on reducing psychotic and negative symptoms and helping individuals, improve day-to-day functioning, and achieve personal life goals, such as completing education, pursuing a career, and having fulfilling relationships.
- Antipsychotic Medications:
Antipsychotic medications constitute the main part of treatment. They can help make psychotic symptoms less intense and less frequent. These medications are usually taken every day in pill or liquid forms. Some antipsychotic medications are given as injections once or twice a month. People respond to antipsychotic medications in different ways. If a person’s symptoms do not improve with one group of antipsychotic medications, they may be prescribed different groups of antipsychotic medication. Many people taking antipsychotic medications experience side effects such as weight gain, dry mouth, restlessness, and drowsiness although with newer available antipsychotics these side effects are less significant.
Sometimes other medications like sedatives can be prescribed for a shorter period of time to manage aggressive/psychotic symptoms.
- Electroconvulsive therapy:
In patients who does not show response to antipsychotics for adequate period of time or patients who have suicidal ideations ECT can be given.