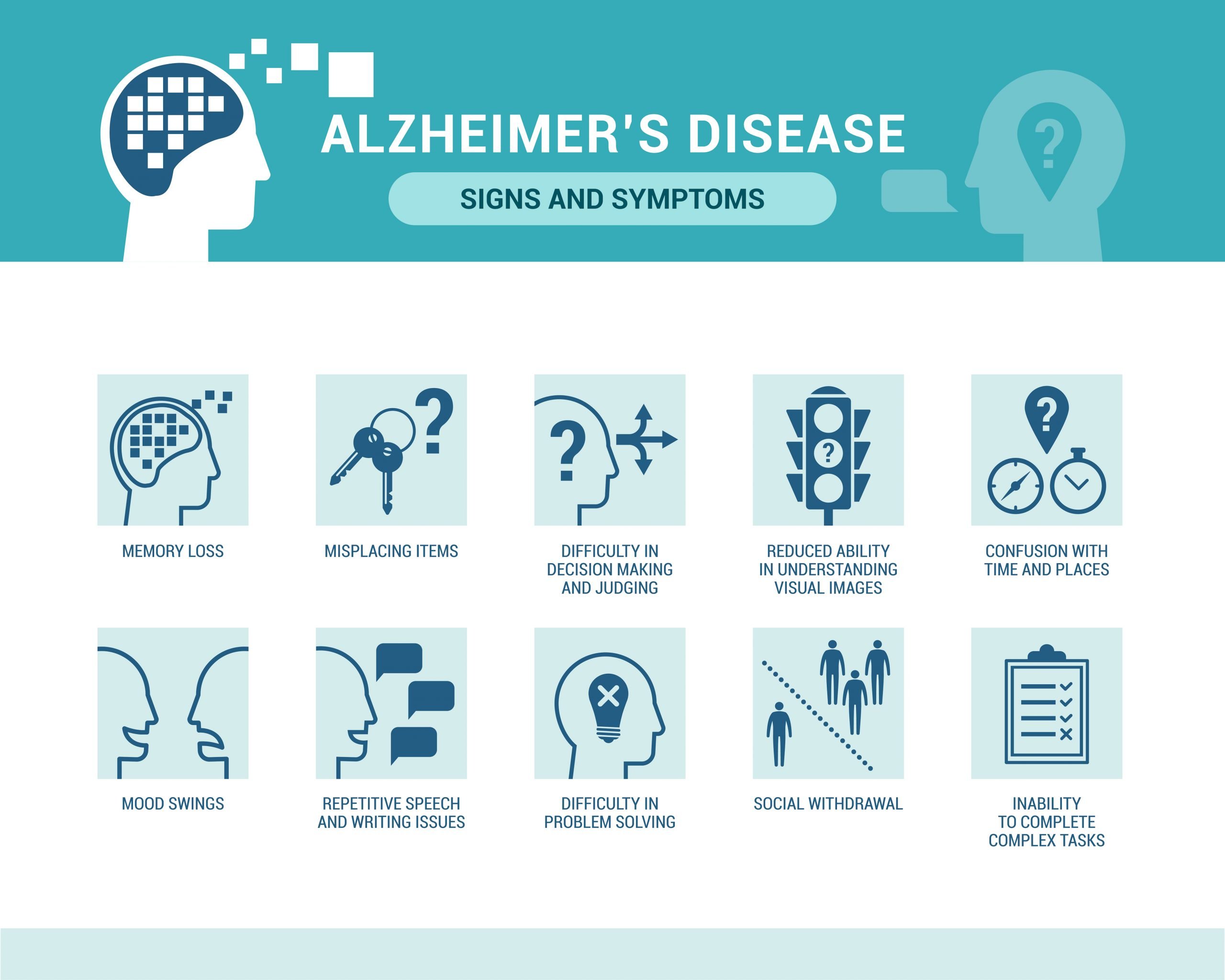
- Asking the same questions over and over again
- Getting lost in places a person knows well
- Forgetting that they have eaten food or taken medicines and asking for food again
- Having trouble following recipes or directions
- Difficulty communicating or finding words
- Difficulty with planning and organising
- Not able to carry out basic tasks which they were well versed with like dressing, writing, bathing
- Repeatedly forgetting family members or relative’s names, or calling them with different names.
Memory Disorders
Acquiring the Best Mental Health and restoring memory disorders for you through proper Diagnosis & Treatment.